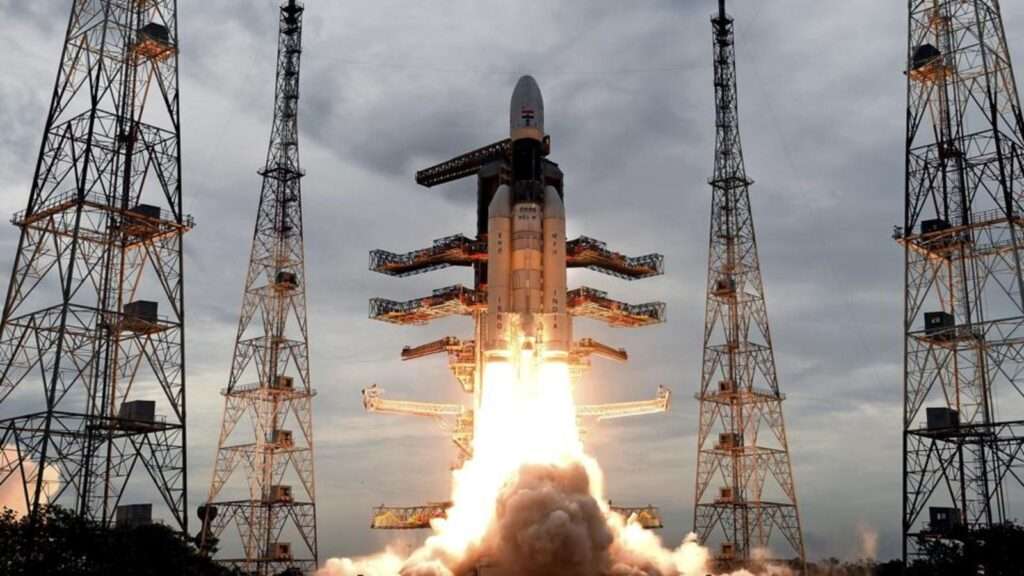
India’s ambitious Earth Observation Satellite (EOS-9) mission faced a major setback as the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) confirmed a launch failure on Sunday due to an unexpected anomaly in the rocket’s second-stage motor. The mission, which was expected to bolster India’s remote sensing capabilities, ended prematurely after what ISRO officials described as a “misbehaviour” in the rocket’s propulsion system.
🚀
Critical Motor Failure Derails Launch
According to an official statement from ISRO, the EOS-9 satellite was aboard the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV-C65), which lifted off from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota at 10:37 IST. However, minutes after launch, telemetry data indicated irregularities in the rocket’s second-stage motor. Engineers observed that the motor failed to deliver the required thrust profile, causing the rocket to deviate from its designated flight path.
The term “misbehaviour” used by ISRO engineers refers to a deviation in expected performance parameters of the solid-fuel motor, possibly due to manufacturing inconsistencies or undetected microfractures in the casing or nozzle assembly. As a result, the mission had to be aborted mid-flight, and the payload could not be placed into its intended sun-synchronous orbit.
🚀
Impact on India’s Satellite Program
The EOS-9 satellite was designed to enhance India’s capabilities in high-resolution Earth imaging, vital for climate monitoring, agricultural forecasting, and disaster response. With this failure, critical data acquisition expected from EOS-9 has been delayed, impacting several government and research initiatives dependent on timely satellite imagery.
The failed launch also marks a rare blemish in the otherwise stellar performance of the PSLV series, which has garnered international acclaim for its reliability and cost-effectiveness. Since its inception, the PSLV has delivered over 300 satellites to orbit, including missions for countries such as the United States, France, and Singapore.
🚀
Root Cause Analysis Underway
ISRO Chairman S. Somanath addressed the media shortly after the incident, stating, “We have constituted a Failure Analysis Committee comprising senior scientists and propulsion experts to thoroughly investigate the cause of the anomaly. The findings will guide future designs and testing protocols to avoid recurrence.”
Initial speculations suggest a fault in the propulsion system’s ignition sequencing or thermal insulation failure, but a detailed investigation is necessary to confirm the root cause. ISRO has also paused the upcoming launches of PSLV until corrective measures are implemented.
🚀
Setback Amid Growing Global Competition
The failure comes at a time when India is scaling up its space operations to compete with global giants like SpaceX, Blue Origin, and China’s CNSA. The private sector has also gained momentum following the liberalization of India’s space economy, with startups like Agnikul Cosmos and Skyroot Aerospace preparing for independent launches later this year.
Experts emphasize that while such failures are a part of the learning curve in space exploration, consistent reliability is key to retaining international trust and satellite launch contracts.
🚀
Conclusion: A Hiccup, Not a Halt
Although the EOS-9 setback is a significant blow to ISRO’s 2025 mission calendar, it also presents an opportunity for introspection and technological refinement. The agency’s swift response and transparency reflect a mature space program committed to safety, accuracy, and continuous improvement.
As India readies for its next set of missions, including Gaganyaan and Chandrayaan-4, the lessons from EOS-9 will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in enhancing system resilience and mission assurance.